
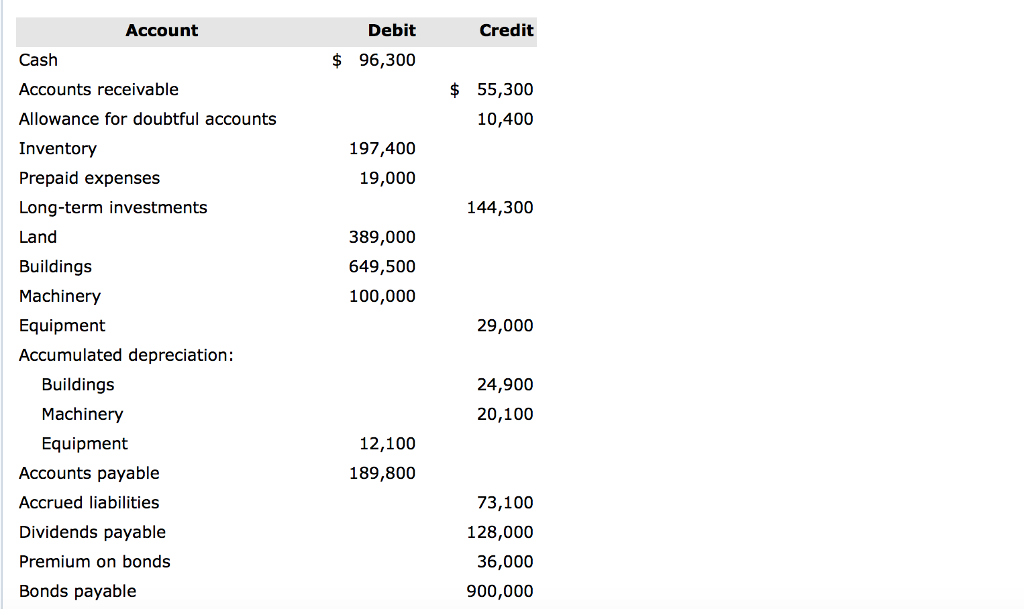
The income statement reflects the changes in a company’s assets, liabilities and equity from its operations over a given period. Double-entry accounting maintains this balance by recording each transaction as a journal entry that balances an equal number of debits and credits.Ī company’s balance sheet is the embodiment of the accounting equation: It reports the value of assets, in balance with its liabilities and equity, at a certain point in time. The accounting equation is a framework that underpins many aspects of business accounting, especially double-entry bookkeeping.

Companies of all sizes use double-entry accounting to run their businesses.ĭouble-entry accounting is required for all public companies, and it’s generally a necessity for businesses that rely on outside financing. This approach reduces the likelihood of accounting errors. Because each journal entry uses both debits and credits, it is said to have two sides - hence the term “double-entry accounting.” What Is Double-Entry Accounting (or Bookkeeping)?ĭouble-entry accounting is a bookkeeping system in which each transaction affects at least two accounts and maintains a balance between debits and credits.
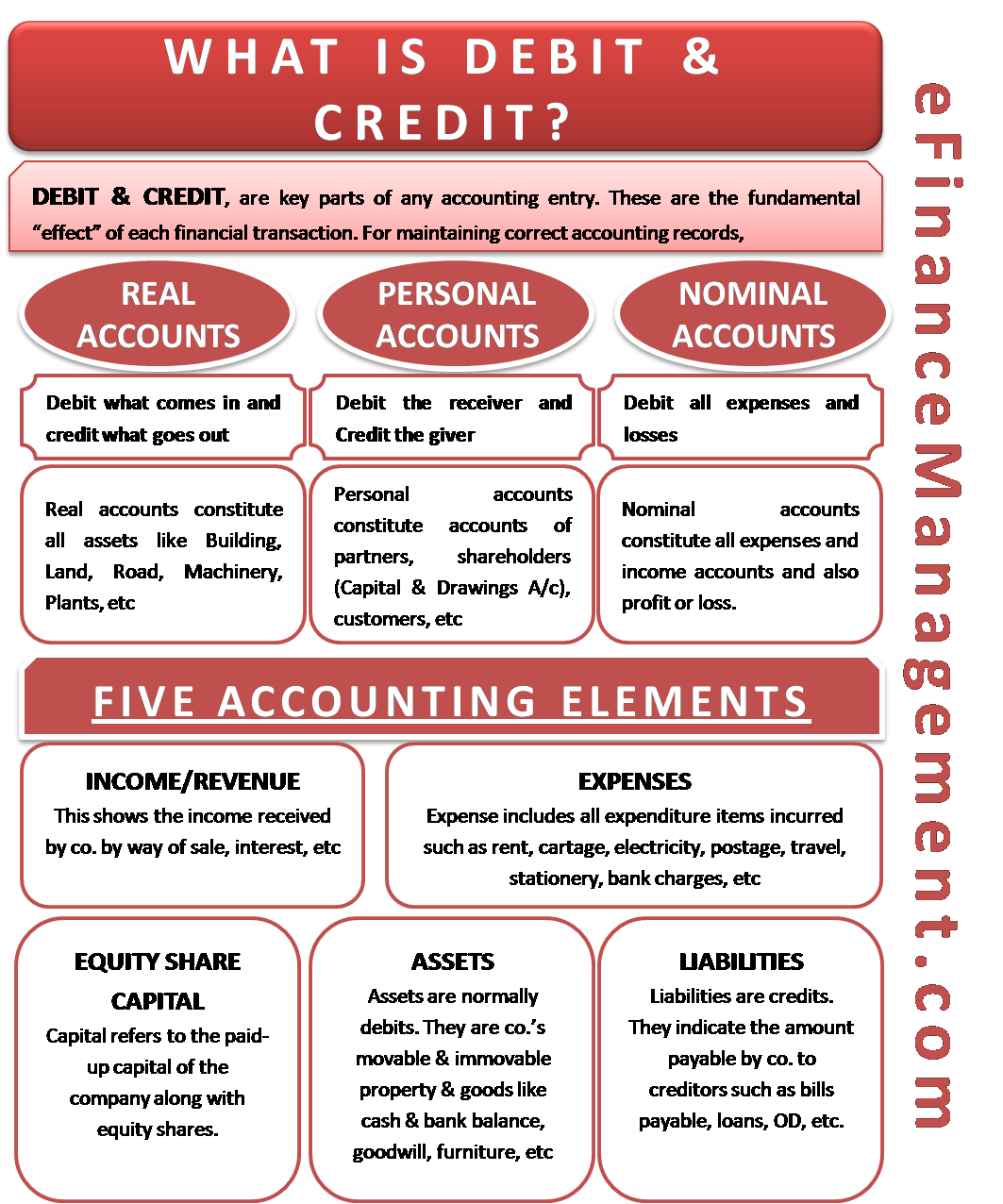
With double-entry accounting, each journal entry updates at least two accounts in the company’s general ledger, using an equal balance of debits and credits to those accounts. Bookkeepers record financial transactions as journal entries that increase or decrease the amount of money in different accounts, depending on the type of transaction. Journal entries are the building blocks of every company’s accounting system. East, Nordics and Other Regions (opens in new tab)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
